2Department of Cardiology, Kocaeli City Hospital, Kocaeli, Türkiye
3Department of Cardiology, Faculty of Medicine, Medipol University, İstanbul, Türkiye
4Center for Coronary Artery Disease, Minneapolis Heart Institute and Minneapolis Heart Institute Foundation, Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA
5Department of Cardiology, Hisar Intercontinental Hospital, Nişantaşı University, İstanbul, Türkiye
Abstract
Background: Currently available risk stratification models for acute pulmonary embolism (PE) include hemodynamic status, cardiac biomarkers, right ventricle (RV) dysfunction on imaging, and clinical scores. Focusing on the length–tension relationship of the ventricle might have a superior predictive capability over RV dysfunction in terms of mortality and classification of patients with acute PE. In this study, our hypothesis suggests that the tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE)/systolic pulmonary artery pressure (sPAP) ratio has superior predictive capability for in-hospital mortality in patients with acute PE compared to TAPSE or sPAP as distinct measures.
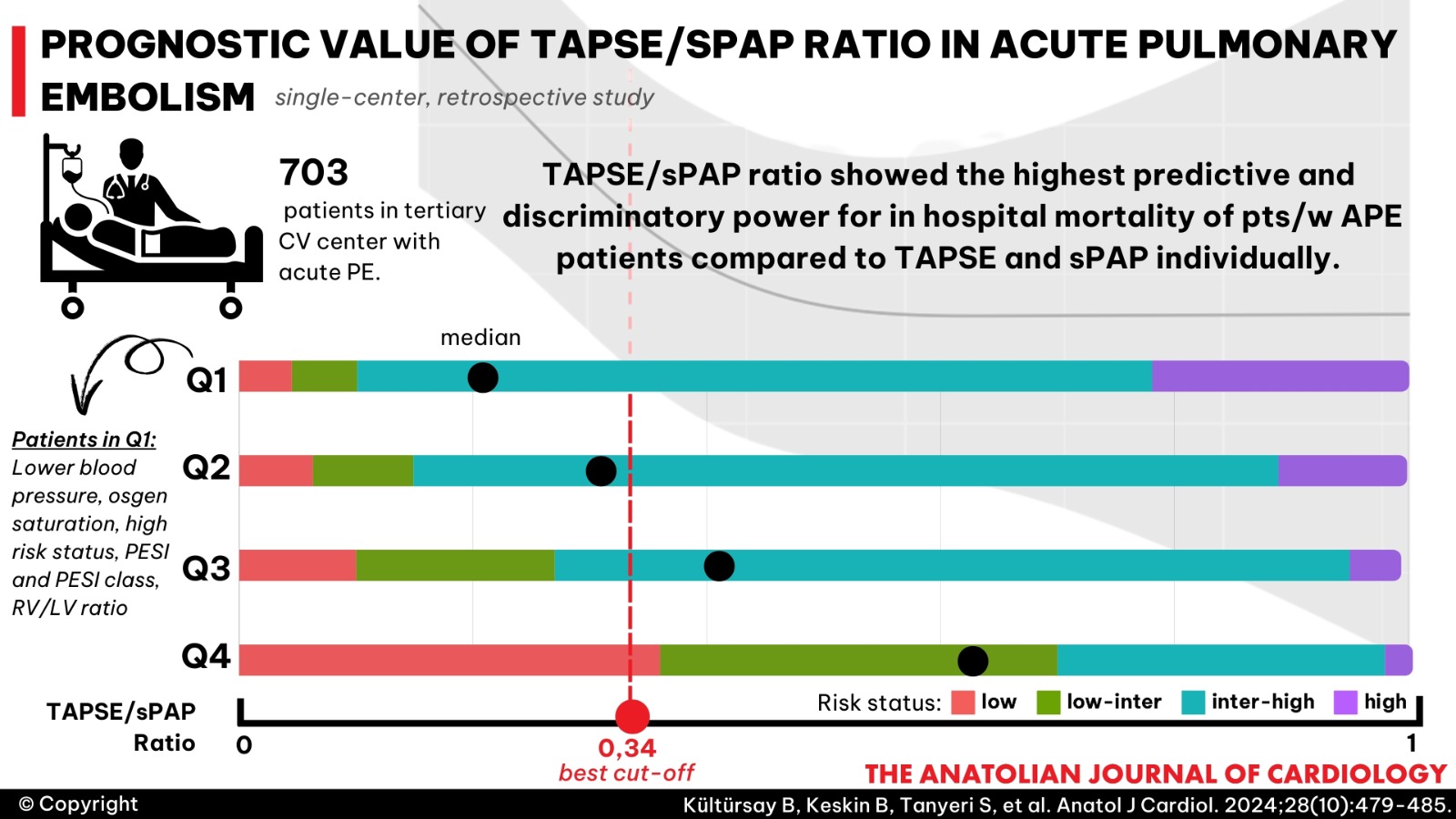
Methods: This single-center study comprised retrospectively evaluated 703 patients referred to our tertiary cardiovascular center with acute PE. We divided patients into quartiles based on the TAPSE/sPAP ratio. Different models were developed to quantify the predictive relationship between in-hospital death and echocardiographic measurements. A base model was created with variables including risk status and RV/LV ratio >1. Then, to evaluate the predictive contribution of each measurement; TAPSE/sPAP, TAPSE, and sPAP were sequentially added to the base model. After that, the performance of each model was evaluated.
Results: Predictive and discriminative power was the highest in model containing TAPSE/sPAP. There was still a significant inverse association between TAPSE/sPAP and the risk of in-hospital death even after adjusting for risk status and RV/LV ratio >1. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis for TAPSE/sPAP revealed the best cut-off value as 0.34.
Conclusion: The outcomes of our study reveal that the ratio of TAPSE/sPAP serves as a more potent predictor of mortality than either of the 2 measurements taken separately. The interpretation and utilization of the TAPSE/sPAP cut-off value in acute PE can assist in identifying patients at risk of deterioration and guide the consideration of more intensive treatment options across all risk groups.
Graphical Abstract
Highlights
- Although right ventricular dysfunction in pulmonary embolism (PE) can be assessed with a transthoracic echocardiogram by TAPSE, tissue Doppler, RV/LV diameter in conjunction with estimated systolic pulmonary arterial pressure (sPAP), its positive predictive value for PE-related death is remarkably low. Hence, there appears to be a need for supplementary prognostic markers.
- The results of this study indicate that the echocardiographic TAPSE/sPAP ratio is not only an independent predictor of in-hospital mortality in patients with acute PE but also exhibits a greater capability of prediction than TAPSE and sPAP measurements individually.
- The interpretation and utilization of the TAPSE/sPAP cut-off value in acute PE can assist in identifying patients at risk of deterioration and guide the consideration of more intensive treatment options across all risk groups.
Introduction
Pulmonary embolism (PE) ranks as the third most prevalent acute cardiovascular syndrome worldwide, following myocardial infarction and stroke.1 In the presence of acute pressure overload and right ventricle (RV) dysfunction, PE can lead to mortality. Currently available risk stratification models using clinical scores, biomarkers, computed tomography (CT), and transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) have been utilized in risk-based treatment strategies in acute PE.2-
Methods
Design
This single-center study retrospectively evaluated 703 patients (median age of 65 years, interquartile range 50-74.3, 57.2% female) referred to our tertiary cardiovascular center with a confirmed diagnosis of acute PE from August 2012 to April 2023. Patients aged <18 years, those with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension, onset of symptoms >14 days, or those receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation were excluded from the study. The systematic work-up for an initial diagnosis of acute PE and risk stratification included multidetector contrast-enhanced CT angiography, TTE assessments, PE severity indexes, and biomarker evaluation, based on criteria recommended by the ESC/ERS PE guideline.1 Acute PE was confirmed by the presence of a thrombus located in at least 1 main or lobar pulmonary artery on CT imaging. All-cause in-hospital mortality, defined as death before discharge, was studied as the primary outcome measure. Local Ethics Committee approval was obtained for the study (Decision date: December 12, 2023, Decision number: 2023/19/752), and the study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Chest CT Pulmonary Angiography
Computed tomography images were acquired using 64-slice helical CT angiography (Toshiba Aquilion 64™, Toshiba Medical Systems Corp., Tokyo, Japan). A validated CT score for pulmonary arterial occlusion proposed by Qanadli et al12 [Qanadli score (QS)], RV/LV ratio, RV diameter, right atrial to left atrial diameter ratio (RA/LA ratio), and main, left, and right pulmonary arterial diameters were measured from CT images. Pulmonary infarction was defined as a peripheral wedge-shaped pulmonary consolidation in a hypoperfused segment of the lung.
Echocardiography
Echocardiography was performed in all patients on the first day of admission using a Vivid-7 echocardiography device (GE Vingmed Ultrasound AS, Horten, Norway). Patients were excluded if the image quality was too poor or if echocardiography could not be performed on the first day of admission. Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion was obtained by positioning an M-mode cursor across the lateral tricuspid annulus and measuring the longitudinal motion of the annulus at peak systole in the standard apical 4-chamber view. The maximal tricuspid regurgitation velocity, obtained using continuous-wave Doppler in accordance with the modified Bernoulli equation, was used in conjunction with the estimated right atrial pressure, measured by the inferior vena cava diameter, to estimate sPAP. Right ventricular lateral annular systolic velocity was obtained using pulsed tissue Doppler, measured on the basal segment of the free wall side of the RV in an apical 4-chamber view. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was calculated using the biplane Simpson’s method. Septal flattening was qualitatively assessed in the emergency department, and the eccentricity index was used in cases with uncertainty. All measurements and assessments were made in accordance with the American Society of Echocardiography guidelines.13
Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using R Studio version 4.3.1 (R Project, Vienna, Austria). Normally distributed continuous data were expressed as mean and SD values, whereas non-normally distributed data were expressed as medians and interquartile ranges. Categorical data were described as absolute and percentage values. The normality of the data was determined using histograms and the Shapiro–Wilk test. Patients were divided into quartiles by TAPSE/sPAP ratio. Regarding sample distribution, analysis of variance and Kruskal–Wallis tests were used for the comparison of continuous data groups according to TAPSE/sPAP quartiles, and Pearson
Results
A total of 703 patients were included in the study (median age: 65, interquartile range: 50-74.3 years, 57.2% female). We divided patients into quartiles by TAPSE/sPAP ratio. The median TAPSE/sPAP values are 0.22, 0.32, 0.42, and 0.63 for Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4, respectively. Baseline clinical characteristics are shown in
In multiple regression analyses, the
Discussion
The present results show that the echocardiographic TAPSE/sPAP ratio is not only an independent predictor of in-hospital mortality in patients with acute PE but also exhibits a greater capability of prediction than TAPSE and sPAP measurements individually. Our findings suggest that as RV–PA coupling deteriorates in patients with acute PE, blood pressure and oxygen saturation decrease, while risk status, PESI, and RV/LV ratio increase.
Assessing the risk of patients with acute PE is crucial for determining the optimal therapeutic management strategy and identifying the notable risk of early mortality.1 Currently, available risk stratification models for acute PE include hemodynamic status, cardiac biomarkers, RV dysfunction on TTE or CT angiography, and clinical scores such as PESI and SPESI.1 The presence of echocardiographic RV dysfunction is associated with short-term mortality even in patients without hemodynamic compromise.8 Focusing on the length–tension relationship of the ventricle may provide superior predictive capability compared to RV dysfunction for classifying patients with acute PE.
In an acute setting, the RV responds to increased afterload with increased contractility. When this homeometric response becomes impaired, the RV resorts to Starling's law, also known as heterometric or dimensional adaptation. This adaptation mechanism increases pulmonary artery pressure and maintains cardiac output.14
Various measurements, including TAPSE/sPAP, fractional area change/invasively measured mean PA pressure, RV area change/end-systolic area, and TAPSE/PA acceleration time, have been suggested as surrogate markers for RV–PA coupling. Guazzi et al15 demonstrated the robust validation and correlation of the TAPSE/sPAP ratio with RV systolic elastance (Ees) and arterial elastance (Ea), establishing its suitability for clinical practice in acute settings. Furthermore, of these measurements, only TAPSE/sPAP emerged as an independent predictor of Ees/Ea in patients with pulmonary hypertension.16 Although invasive pressure–volume analysis is considered the gold standard for assessing RV–PA coupling, it is not applicable in evaluating patients with acute PE. Therefore, TAPSE/sPAP, a non-invasive and inexpensive correlate of pressure–volume analysis, might have clinical relevance in evaluating RV dysfunction in patients with acute PE.
Recently, Falsetti et al17 reported that in intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism, the TAPSE/sPAP ratio independently predicts mortality to a greater extent than CT angiography and troponin. Similarly, Lyhne et al18 published a retrospective analysis of a pulmonary embolism registry from a single center, including 627 patients. They have indicated that the TAPSE/sPAP ratio can predict short-term adverse outcomes in acute PE. Our retrospective single-center analysis confirms these findings, with a larger and more heterogeneous sample size, including all risk groups and patients treated with CDT and low-dose fibrinolytic drugs.
Based on the ROC curve analysis of our model, the optimal cut-off value of TAPSE/sPAP, determined by the Youden index, was 0.34. This cut-off is comparable to the previously suggested value of 0.4 by Lyhne et al18 and 0.31 for patients with pulmonary hypertension.16 Moreover, our analysis still shows a significant inverse association between TAPSE/sPAP and the risk of in-hospital death even after adjusting for risk status in our analysis (change from 0.27 to 0.50, OR = 0.36, 95% CI: 0.20-0.64,
Study Limitations
In this study, we retrospectively analyzed our single-center data containing a large population of patients. This heterogeneous population includes all risk groups and treatment modalities; therefore, generalizability is not limited. However, a prospective study is needed to define a more accurate TAPSE/sPAP cut-off value to guide aggressive treatments such as CDT in intermediate and intermediate-high-risk groups. Major limitations of echocardiographic evaluation are observer dependency and assessment of RV function. We performed TTE on the first day of presentation; using TAPSE to evaluate RV function may reduce observer dependency and increase reliability and simplicity in acutely presented patients. It is important to highlight that the calculated sPAP is derived from the TR jet using the modified Bernoulli's formula, which may underestimate sPAP in patients with severe TR, constituting significant limitations of the study. Additionally, TAPSE might be overestimated in this particular group of patients. Although using TAPSE/sPAP in this patient group might lead to misleading conclusions, only a small proportion of patients with acute PE present with severe TR. Another limitation is that TAPSE might not reflect the global function of the RV as it only represents longitudinal systolic motion of the RV.
Conclusion
The outcomes of our study reveal that the ratio of TAPSE/sPAP serves as a more potent predictor of mortality than either of the 2 measurements taken separately. The interpretation and utilization of the TAPSE/sPAP cut-off value in acute PE can assist in identifying patients at risk of deterioration and guide the consideration of more intensive treatment options across all risk groups.
Footnotes
References
- Konstantinides SV, Meyer G, Becattini C. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur Heart J. 2020;41(4):543-603. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehz405
- Elias A, Mallett S, Daoud-Elias M, Poggi JN, Clarke M. Prognostic models in acute pulmonary embolism: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2016;6(4):e010324-. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010324
- Külahçıoğlu Ş, Tokgöz HC, Akbal ÖY. Eosinophil-to-monocyte ratio as a candidate for a novel prognostic marker in acute pulmonary embolism: is it a consumptive mechanism?. Anatol J Cardiol. 2022;26(9):717-724. https://doi.org/10.5152/AnatolJCardiol.2022.1780
- Türkday Derebey S, Tokgöz HC, Keskin B. A new index for the prediction of in-hospital mortality in patients with acute pulmonary embolism: the modified shock index. Anatol J Cardiol. 2023;27(5):282-289. https://doi.org/10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2023.2530
- Pruszczyk P, Goliszek S, Lichodziejewska B. Prognostic value of echocardiography in normotensive patients with acute pulmonary embolism. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014;7(6):553-560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmg.2013.11.004
- Meinel FG, Nance JW, Schoepf UJ. Predictive value of computed tomography in acute pulmonary embolism: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2015;128(7):747-59.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2015.01.023
- Keskin B, Tokgöz HC, Akbal ÖY. Clinical, imaging and hemodynamic correlates and prognostic impact of syncope in acute pulmonary embolism: a single-center study. Turk Gogus Kalp Damar Cerrahisi Derg. 2022;30(3):317-326. https://doi.org/10.5606/tgkdc.dergisi.2022.22798
- Coutance G, Cauderlier E, Ehtisham J, Hamon M, Hamon M. The prognostic value of markers of right ventricular dysfunction in pulmonary embolism: a meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2011;15(2):R103-. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc10119
- Tello K, Axmann J, Ghofrani HA. Relevance of the TAPSE/PASP ratio in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Int J Cardiol. 2018;266():229-235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.01.053
- Guazzi M, Bandera F, Pelissero G. Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion and pulmonary arterial systolic pressure relationship in heart failure: an index of right ventricular contractile function and prognosis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013;305(9):H1373-H1381. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00157.2013
- Acar RD, Acar Ş, Doğan C. The TAPSE/PASP ratio and MELD score in patients with advanced heart failure. Das TAPSE/PASP-Verhältnis und der MELD-Score bei Patienten mit Fortgeschrittener Herzinsuffizienz. Herz. 2021;46(suppl):75-81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00059-019-04879-x
- Qanadli SD, El Hajjam M, Vieillard-Baron A. New CT index to quantify arterial obstruction in pulmonary embolism: comparison with angiographic index and echocardiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;176(6):1415-1420. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.176.6.1761415
- Rudski LG, Lai WW, Afilalo J. Guidelines for the echocardiographic assessment of the right heart in adults: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography endorsed by the European Association of Echocardiography, a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology, and the Canadian Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2010;23(7):685-78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.echo.2010.05.010
- Vonk Noordegraaf A, Westerhof BE, Westerhof N. The relationship between the right ventricle and its load in pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;69(2):236-243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2016.10.047
- Guazzi M, Dixon D, Labate V. RV contractile function and its coupling to pulmonary circulation in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: stratification of clinical phenotypes and outcomes. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017;10(10 ):1211-1221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmg.2016.12.024
- Tello K, Wan J, Dalmer A. Validation of the tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion/systolic pulmonary artery pressure ratio for the assessment of right ventricular-arterial coupling in severe pulmonary hypertension. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019;12(9):e009047-. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.119.009047
- Falsetti L, Marra AM, Zaccone V. Echocardiographic predictors of mortality in intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism. Intern Emerg Med. 2022;17(5):1287-1299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-021-02910-w
- Lyhne MD, Kabrhel C, Giordano N. The echocardiographic ratio tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion/pulmonary arterial systolic pressure predicts short-term adverse outcomes in acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021;22(3):285-294. https://doi.org/10.1093/ehjci/jeaa243
- Kaymaz C, Akbal OY, Hakgor A. A five-year, single-centre experience on ultrasound-assisted, catheter-directed thrombolysis in patients with pulmonary embolism at high risk and intermediate to high risk. EuroIntervention. 2018;14(10):1136-1143. https://doi.org/10.4244/EIJ-D-18-00371
- Kaymaz C, Akbal OY, Keskin B. An eight-year, single-center experience on ultrasound assisted thrombolysis with moderate-dose, slow-infusion regimen in pulmonary embolism. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2022;20(4):370-378. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570161120666220428095705
- Kaymaz C, Öztürk S, Akbal Ö. Ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis in high-risk and intermediate-high-risk pulmonary embolism: results from a single-center cohort. Angiology. 2017;68(5):433-440. https://doi.org/10.1177/0003319716661446
- Akbal ÖY, Keskin B, Tokgöz HC. A seven-year single-center experience on AngioJet rheolytic thrombectomy in patients with pulmonary embolism at high risk and intermediate-high risk. Anatol J Cardiol. 2021;25(12):902-911. https://doi.org/10.5152/AnatolJCardiol.2021.28303
- Kaymaz C, Tokgöz HC, Kültürsay B. Current insights for catheter-directed therapies in acute pulmonary embolism: systematic review and our single-center experience. Anatol J Cardiol. 2023;27(10):557-566. https://doi.org/10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2023.3639


